One of the most valuable brands in the world, Google and its products have always fascinated me. In this article, I have analysed the business strategy of Google within the Online Advertising Industry.
Google’s diverse range of products and services means that we need to narrow our focus to a specific industry to comprehensively discuss its business strategy.
As Google generates substantially all of its revenues from advertising (86% in 2017, 91% in 2013), it’s appropriate to consider Google as an advertising business and look at its business strategy specifically within the online advertising industry.
Although Google is heavily investing in areas such as digital content, enterprise cloud services, and hardware products, at its core, it is an advertising business that generates most of its revenue primarily by delivering both performance advertising and brand advertising.
Introduction
This article presents the business level strategy of Google within the online advertising industry.
First, a short overview of the online advertising industry is presented. Second, the competitive environment of Google is evaluated with evidences and its core competencies, and the key future challenges are pointed out. Third, the key business strategies of Google over the past five years are identified in the article.
The strategies are then evaluated using Porter’s generic strategies and discussed why those strategies were pursued or changed.
Finally, the strategies are evaluated by matching with the resources and capabilities of Google in terms of Suitability, Feasibility, and Acceptability.
Overview of the Online Advertising Industry
The online advertising industry is a high-growth and fast-paced industry accounting for more than 100 billion dollars in revenue worldwide (Emarketer.com, 2013).
The industry is growing faster with the increasing use of Internet-based advertising to reach more targeted customers with methods such as online display advertising, search engine marketing, mobile advertising, social media advertising, etc.
The Ad revenue figures show a steady growth of the industry in recent years with a higher growth rate projected in the upcoming years.
Forecasting a compound annual growth rate of 7.3% during 2013-2018, a Research and Markets (2013) report on the Global online advertising industry 2013-2018 reports that consumer behaviour and shift towards digital media trends are key drivers of the industry.
Other key factors driving the industry include economic stability, growing mobile users and increasing Internet accessibility. Government Internet regulations, censorship, and online privacy are the major challenges of the industry.
Competitive Environment of Google – Overview
Google is a technology company with products and services that help users provide and connect with information. The company’s visionary mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.
Core services from Google include search and display advertising, the Android operating system platform, consumer content through Google Play, enterprise, commerce and hardware products (Google Annual Report, 2013).
With a variety of its tools and services, the main value proposition Google tries to deliver as per its business model is targeted online advertising.
Google provides services such as AdWords and AdSense to advertisers that help them reach targeted customers in a cost-effective way and in return help the company generate its revenue from those advertisers.
The process is made possible by its popular search engine which facilitates the entire advertising business model.
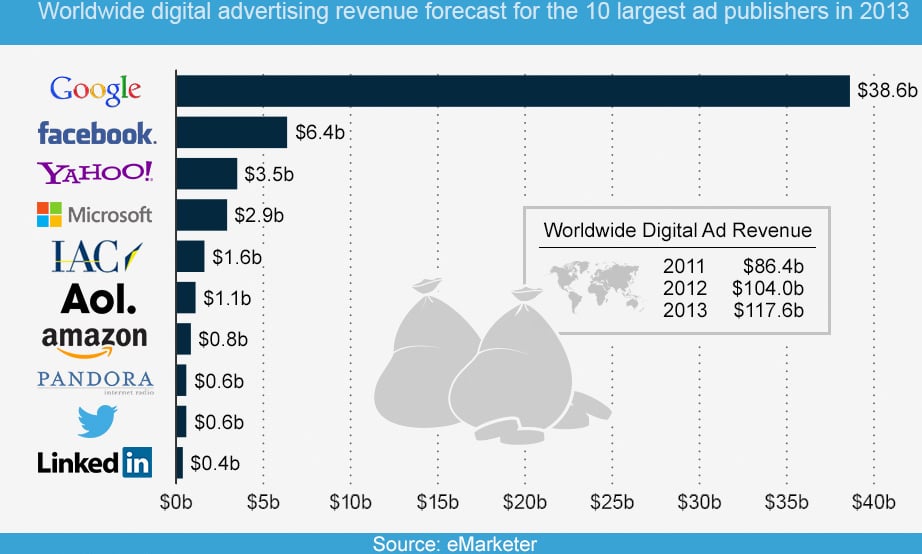
Competitive Environment of Google
Google, Facebook, Yahoo!, Microsoft, and IAC are the top five players in the industry accounting for more than 40% of the global online advertising revenue in 2013 (Appendix A).
Search and Mobile advertising are strong sectors within the industry. Although search and display advertising are current leading advertising formats, the mobile’s excessive growth will level the gap in upcoming years.
Besides, social media advertising is completely changing the way advertisers target their customers and thus affecting the industry as a whole.
The rapid growth of social platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn is making them capable of challenging and competing with other traditional online advertising companies, which can be taken as a future trend of online advertising.
Google is clearly a leader in the online advertising landscape seizing almost a third of the market share. Google’s core competency in the industry includes its fast and efficient search engine that accounts for almost 70% of the search engine market share followed by Baidu, Yahoo, and Bing (Netmarketshare, 2014).
Smart, complex, and constantly updated algorithms help keep its search engine at the forefront of the industry.
The search engine, however, is available for free for its users and what generates the revenue is paid listings and advertisements on the search pages.
Two of Google’s innovative products responsible for advertising i.e. Adwords and Adsense have created a competent advertising ecosystem that makes use of its massive search engine users. Google continues to dominate both search and mobile, a tremendously growing niche within the online advertising industry.
The company is already a leader in search market share for several years and has also seen tremendous growth in mobile advertising in recent years. Google’s popular mobile platform – Android makes it possible to excel in the mobile sector of online advertising.
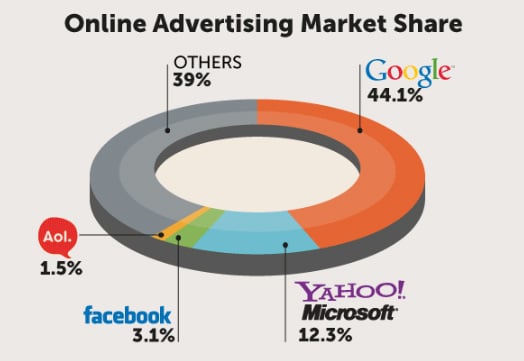
The key future challenges of Google are maintaining a strong brand image, complying with future government laws and regulations, protecting technological intellectual properties, addressing privacy concerns of the growing user base, successful international operations and expansion, retaining key business personnel and maintaining the overall culture of the business (Google Annual Report, 2013).
Google Business Strategy
Porter (1985) suggests three generic strategies that businesses can adopt to achieve and maintain competitive advantage i.e. cost leadership, differentiation, and focus.
Evaluating Google’s unique products and services and their different segments of customers, it’s clear that the company is following a differentiation strategy in terms of Porter’s framework. Google’s huge technology infrastructure, a wide range of innovative products, and a greater market share give the firm a competitive advantage in the industry.
The company has gained a sustained competitive advantage by outperforming other competitors such as Yahoo, Microsoft, and Aol for a long time and maintaining a high share of the online advertising industry.
Google’s former CEO Eric Schmidt in an interview said that the company doesn’t have a five-year plan and rather focuses on what’s new and exciting (Carlson, 2009).
Google indeed believes in the free flow of ideas and its strong and unique culture has fueled innovation in several aspects of Google’s works.
Speaking onstage at TED 2014, Google’s CEO Larry Page revealed several future plans of Google. Larry’s views in the video provide us with several insights to Google business strategy in the future.
Page’s plan for Google includes changing the world with technology by fulfilling visionary goals such as making the internet available to the entire population and exploring possibilities with innovative projects such as Google self-driving car and Google Glass among others (TED, 2014).
In an article, Forbes quotes Search strategist AJ Kohn to explain Google’s strategy in the simplest terms “Get people to use the Internet more” in addition relates all the latest innovative products of Google to the strategy of encouraging people to spend more time online and thus generate more revenue from it (Kosner, 2013).
The key strategies of Google, as perceived from its focus and actions in the past five years along with its analysis of where the company is heading next are discussed below.
Increasing Internet Accessibility
Google’s main focus is to gain more Internet users as the company’s revenue depends on more and more people using its search engine and other services.
Be that with new and improved products or visionary projects like Project Loon, Google is mostly concerned with reaching a wider population on the planet by expanding Internet accessibility.
Focusing on the fact that two-thirds of the world’s population are yet to have access to the Internet, Google’s Project Loon balloons help connect remote and rural areas with access to online information (Google.com, 2014).
Google’s CEO, Larry Page at TED 2014 reveals that he has been thinking about the idea of providing global Internet access for the last five years and he is really excited about Project Loon.
A recent acquisition of Titan Aerospace, a high-altitude drone maker by Google is also an indication of how serious Google is about the project.
According to BBC, Google said that Titan Aerospace would facilitate its Project Loon in making the Internet accessible to a wider population (BBC News, 2014).
Google’s other project, Google Fiber, which provides a hundred times faster Internet has changed the way people use the internet for entertainment purposes among other usages of the powerful Wi-Fi.
Rolled out in a few US cities already, the company is providing basic Internet free with additional costs for higher speed and its TV services (Fiber.google.com, 2014).
Google faces a threat from ISPs (Internet service providers) that may disrupt the accessibility of Google services to its users. The company itself being the internet service provider, in the long run, will secure its users and advertisers.
Innovative projects such as Project Loon and Google Fiber, Google is working on are unique products and, therefore, the company follows a differentiation strategy.
Improving Search Infrastructure
Search products are the core offerings of Google and are directly related to advertising, the main revenue stream of the company.
The company built its brand on basis of a powerful search engine offering advertisement opportunities on the search pages matching the keywords of the search engine users.
Google revealed that it spends more than 70% of its resources on building and improving its search and advertising products and this can be easily justified by looking at continuous changes in its portfolio of related products.
Innovating in search products and services so that they can sustain search advertising revenue has been of significance to the company.
Expanding the domain of search infrastructure the company is also focusing on its products such as Google Chrome which help users browse the web with faster speed and with greater security and privacy.
With more than 750 million users (Google Annual Report, 2013), Google is trying to create another ecosystem with its chrome apps and users.
Charles Golvin, an analyst with a research company, Forrester argues that Google is pushed to search for expensive advertising and its focus on several platforms such as Chrome is all advertisement driven so that it can offer higher price advertising to its main customers – advertisers (Keizer, 2014).
Google is constantly expanding its search services and wants to innovate the search process with improved knowledge graphs backed with artificial intelligence technologies.
All these activities are distinct from its competitor Facebook, Amazon and others that have built search facilities along other domains of the social graph, personal relationships, and the product.
Improving Mobile Products and Advertising Solutions
Announcing the first-quarter earnings of 2014, Google’s CEO and founder Larry Page said that a lot of improvements were done in mobile products in the past quarter (Google, 2014).
This clearly reveals the focus of Google to be a strong player in the mobile market and make mobile a core part of its strategy.
The first quarter results although increased in comparison with the first quarter of 2013, weren’t in line with the predictions. In addition, the decreasing percentage in cost-per-click that Google charges to its advertisers became a concern considering Google’s inability to charge advertisers higher prices for mobile ads (BBC, 2014).
Google and the entire online advertising industry are struggling to monetize mobile devices including new smartphones and tablets.
Mobile’s tremendous growth is not a surprise to Google but the company has yet to master mobile advertising matching to its desktop counterpart.
Google’s chief business officer believes that the mobile advertising rates will eventually be better than the desktop prices citing the fact that context and location are important aspects of mobile advertising (Edwards, 2014).
It’s indeed a difficult time for Google to convince its mobile advertisers to pay a higher price for Ads because of their poor conversion and this will need some serious work from the company as its business is shifting more towards mobile.
Apart from search and advertising solutions on mobile, Google’s focus is also on growing and keeping ahead of its competitors in smartphone platforms.
Mobile platform Android, led by Google dominates the market occupying 52.1% of the OS market, slightly ahead of Apple with 41.3% as of February 2014 (comScore Reports, 2014).
The platform, as reported in corporate highlights of Google’s annual report (2013) crossed one billion users as of September 2013.
Google has built a complete ecosystem of a smartphone market with Android and continues to invest huge time and effort in improving the open-source platform to provide a better mobile experience to its users.
Android is different from other mobile platforms being open source and free for hardware manufacturers, differentiating its offering from other paid and manufacturer-restricted platforms.
Google also follows a differentiation strategy in terms of providing unique search advertising facilities to advertisers on its top mobile properties.
Focus on Social Networks and Social Advertising
Social platforms like Facebook and Twitter which quickly soared on the advertising landscape have urged Google to pursue its social platform strategy seriously.
The company might have failed several times with its social strategy in the past, but it looks like it is finally gaining traction with its social platform called Google+ launched in November 2011.
The company forced its other platform users such as Gmail and YouTube to be part of the platform and this has added users aggressively on Google+ to surpass Twitter user numbers.
Forrester, a market research company as reported by Edwards (2014), has revealed fresh insights in terms of user engagement and conversions comparing Social platforms Facebook, Twitter, and Google+.
Stating the fact that Google+ has got the user engagement boost from the usage of its search engine, Edwards (2014) argues that the social platform is now a potential threat to other platforms like Twitter and Facebook for social advertisements.
Apart from influencing brands and businesses to join the platform, Google+ recently announced a new type of social Ads called +Post ads on their product updates page that advertisers can use to turn their updates into engagement ads (Google, 2014).
The new social advertisement feature is similar to Facebook and Twitter advertisements in the sense that businesses can now amplify the reach of their posts across the social web.
Resources and Capabilities of Google
Grant (2010) defines resources as productive assets of an organization and capabilities as what an organization can do using the resources adding the fact that all resources must act together to form the capabilities of an organization.
The principal type of resources in terms of tangible, intangible, and human resources for Google in reference to the above strategies are discussed with further evidence below.
Resources of Google
Exceptional Products and Financial Resources – Tangible Resources
Tangible resources have physical attributes and are visible to an organization (Rothaermel, 2013).
Google has a huge technology infrastructure that supports a portfolio of exceptional products that can be used by agencies and other businesses for their online advertising activity.
Google’s wide range of advertising products includes AdWords, Adsense, DoubleClick Ad Exchange and other platforms that advertisers can benefit from are Google’s network member websites and Google-owned websites including Google Finance and Youtube (Google Annual Report, 2013).
Google’s multibillion-dollar infrastructure includes its data centres in several locations in the US and a few other countries that power its products (Levy, 2014).
Google also has a strong financial performance over years and this has generated huge financial resources for the company.
In the recent annual statement as of March 31, 2014, Google reported 59.38 billion dollars as its cash and cash equivalents (Google Q1 Results, 2014).
Google’s Culture and Brand – Intangible Resources
Google has an open and entrepreneurial culture, mostly resembling the culture of start-ups where everyone’s ideas are valued and everyone on the team is made comfortable sharing their opinion (Google.co.uk, 2014).
The company’s structure is non-hierarchical and flat which allows collaboration between teams and makes the leadership position easy to approach.
Google’s culture also serves as an ideal medium to foster the company’s innovation and, in fact, several innovative products of the company can be credited to its culture (Economist, 2009).
Google maintains a strong brand reputation among its users, advertisers and partners. The company has a reputation as one of the top brands in the world and the best place to work. Google was Fortune’s top company to work for in the latest ranking report of 2014 (CNN Money, 2014).
Google’s valuable intellectual properties such as trademarks and patents are also worth considering under the intangible resources of the company.
Google’s Employees and Skills – Human Resources
Google spends significant efforts in hiring, retaining and motivating its skills force.
The company considers its key personnel and services essential for long-term vision and crucial to implement its business strategies (Google Annual Report, 2013).
Google competes with several other tech companies such as Microsoft, Facebook and Yahoo for its employees and makes sure it can retain those employees for a long time at Google.
The company hires the best engineers with its reputation as one of the best places to work and builds a strong and motivated workforce that is culturally fit to the company and is immensely productive.
Capabilities of Google
Google’s resources on its own are not sufficient to get the tasks done. Its capabilities make use of those resources to gain competencies in what Google does very well.
The management practices of Google’s executive team and the top performance of Google’s engineers matched with world-class resources add to the capabilities of what Google can actually achieve.
The company’s culture enables its employees to work on several ideas even beyond their job responsibilities and this helps fuel innovation capabilities at Google.
The strong financial resources of Google also provide it with the capability of acquiring several startups and the genius minds behind those startups.
Evaluation of Strategies in terms of Resources and Capabilities
The strong capabilities and comprehensive resources of Google make it possible to carry forward its strategies with ease.
The company often exceeds its target of realistic goals and tries to get closer to its long-term visionary goals.
In terms of strategies discussed above in section 3.0, the company is making real progress with most of its strategies and this is justified by the company’s growing market share and users of its different services.
Thanks to its financial resources, the company has acquired companies like Titan Aerospace to make its strategy of increasing Internet accessibility successful.
The constant innovation of Google in its products and services has made it possible for billions of people as of September 2013 to adopt its mobile platform and this growth will definitely make its mobile strategy successful.
Google’s investment in research and development with its skilled and top-notch engineers (human resources) will help the company eventually come up with innovative products that will solve big problems in advertising and in other sectors.
Evaluation of Strategies in terms of SFA
Suitability of Strategies
Suitability helps to evaluate the strategies of an organization in terms of addressing the key opportunities and threats of the organization (Johnson et al, 2011).
Google’s strength lies in its popular search engine and strategies discussed above such as improving search infrastructure directly relates to building on Google’s strength.
The company is facing threats from social networking giants like Facebook and Twitter that are quickly gaining the traction in the online advertising landscape.
Google’s strategy of growing its social network and social advertising minimises the threat from those competitors and at the same time, urges to move in direction of where advertising might be going in future.
Feasibility of Strategies
Feasibility assists in evaluating strategies on basis of the organization’s capability to accomplish it (Johnson et al, 2011).
Google’s strategies are indubitably farsighted but the organization’s powerful resources would make most of it feasible in the long term.
The company expects to hire people aggressively, acquire more startups and invest heavily in its infrastructure to build the strengths of its resources and all these resources will work towards delivering the company’s strategy.
Increasing revenue and profits in recent years also display that Google’s strategies have been feasible.
Acceptability of Strategies
Acceptability helps us evaluate strategies considering the outcomes of strategies and if they have actually met the expectations of stakeholders (Johnson et al, 2011).
Google’s latest financial results as of the first quarter of 2014 have disappointed investors and this shows that Google is struggling to fulfil stakeholders’ expectations of estimated growth.
Besides, Google’s strategy of diversifying its product portfolio is worrying its investors that the company is not focusing on the core part of its business i.e. advertising.
Google’s stakeholders, however, have faith in the innovation of the company as the company has built a reputation for incredible achievements in the past.
Conclusion
Google has seen some crucial changes in its focus, culture and strategy after its co-founder Larry Page succeeded Eric Schmidt as CEO of the company in April 2011.
Under Page’s leadership, who now leads the development and technology strategy, Google’s focus is more on improving fewer products, pursuing innovative ideas, and maintaining the culture of Google.
The company generated 91% of its revenue from advertisers as reported in its annual report of 2013 and will continue to be an online advertising industry giant with its successful social and mobile strategies in upcoming years.
Please note that the original article was written in 2014 and is continuously updated with new links. Google’s complex and ever-evolving business, however, means that the specifics of its strategy also continuously keep changing.
Feel free to use the above academic framework and resources to work on the latest business strategy of Google.
